Domain Name System (DNS) commands are essential tools for system administrators, cybersecurity professionals, developers, and network engineers. They help diagnose DNS issues, verify records, trace resolution paths, and gather intelligence about domains and IP addresses.
This article covers the most commonly used DNS commands – `host`, `dig`, and `whois`with practical examples for each.
- Host Command Examples
- Basic Domain Lookup
- Query A Record (IPv4)
- Query AAAA Record (IPv6)
- Query Mail Exchange (MX) Records
- Query Name Server (NS) Records
- Query TXT Records
- Query Canonical Name (CNAME)
- Query Start of Authority (SOA)
- Query Using a Specific Name Server
- Reverse Lookup Using Domain and IP
- Display All Available Records
- Query ANY Record Type
- Reverse DNS Lookup
- Verbose Output
- DIG Command Examples
- Trace DNS Resolution Path
- Short Output
- Display Only Answer Section
- Reverse Lookup (PTR)
- Name Server Search
- Minimal A Record Output
- WHOIS Command Examples
- Domain WHOIS Lookup
- IP Address WHOIS Lookup
1. Host Command Examples
The `host` command is a simple and fast DNS lookup utility used to resolve domain names to IP addresses and retrieve DNS record information.
1.1 Basic Domain Lookup
To resolve a domain name to its associated IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, the command is:
host example.com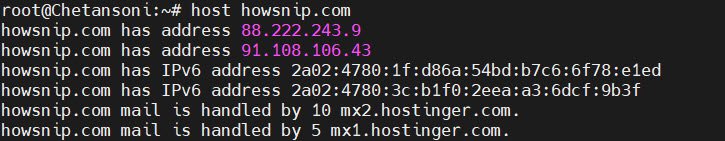
1.2 Query A Record (IPv4)
To retrieve the IPv4 (A) record for any domain, the command is:
host -t a example.com
1.3 Query AAAA Record (IPv6)
In case, if you want to fetch the IPv6 (AAAA) record, then the command is:
host -t aaaa example.com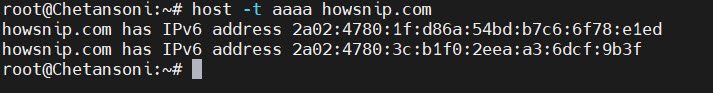
1.4 Query Mail Exchange (MX) Records
To display mail servers responsible for receiving email for any domain, the command is:
host -t mx example.com
1.5 Query Name Server (NS) Records
To lists authoritative DNS name servers, you can run the following command:
host -t ns example.com
1.6 Query TXT Records
For retrieving TXT records commonly used for SPF, DKIM, and domain verification, the command is:
host -t txt example.com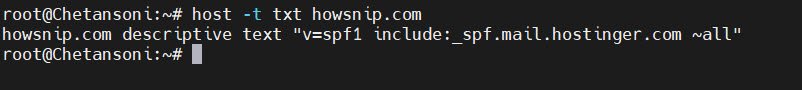
1.7 Query Canonical Name (CNAME)
To check whether a subdomain is an alias pointing to some another domain, the command is:
host -t cname www.example.com
1.8 Query Start of Authority (SOA)
To display authoritative DNS zone information, including serial number and admin email, the command is:
host -t soa example.com
1.9 Query Using a Specific Name Server
To force the query to be resolved using a specific DNS server, you can use the following command:
host example.com ns1.example.com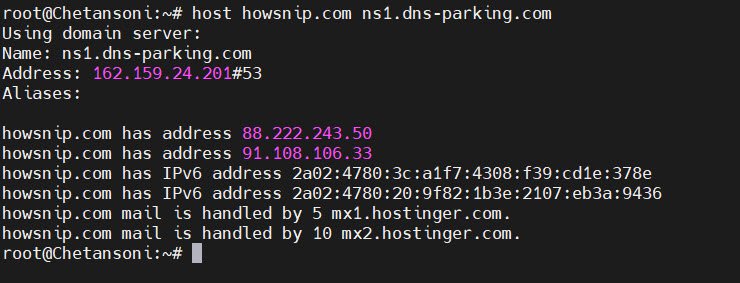
1.10 Reverse Lookup Using Domain and IP
To check forward and reverse DNS mappings together, the command is:
host domain.com ip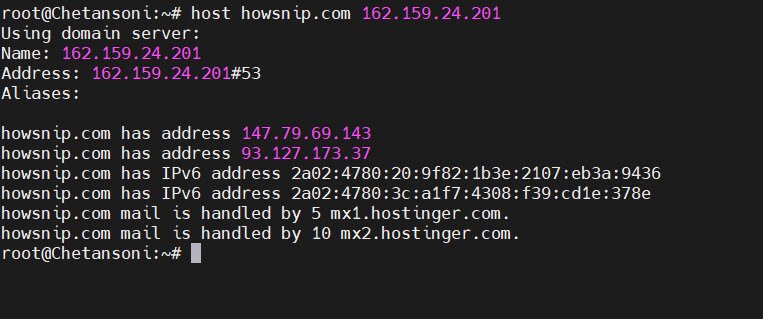
1.11 Display All Available Records
To perform an extensive DNS query which returns all record types, the command is:
host -a example.com
1.12 Query ANY Record Type
To request all DNS record types, the command is:
host -t any example.com
1.13 Reverse DNS Lookup
To resolve an IP address back to a hostname (PTR record), the command is:
host ip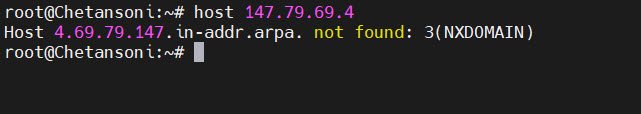
1.14 Verbose Output
To display detailed query and response information for troubleshooting, the command is:
host -v -t a example.com2. DIG Command Examples
The `dig` (Domain Information Groper) command is a powerful DNS diagnostic tool offering precise control over DNS queries.
2.1 Trace DNS Resolution Path
To trace the full DNS resolution path from root servers to authoritative servers, the command is:
dig +trace example.com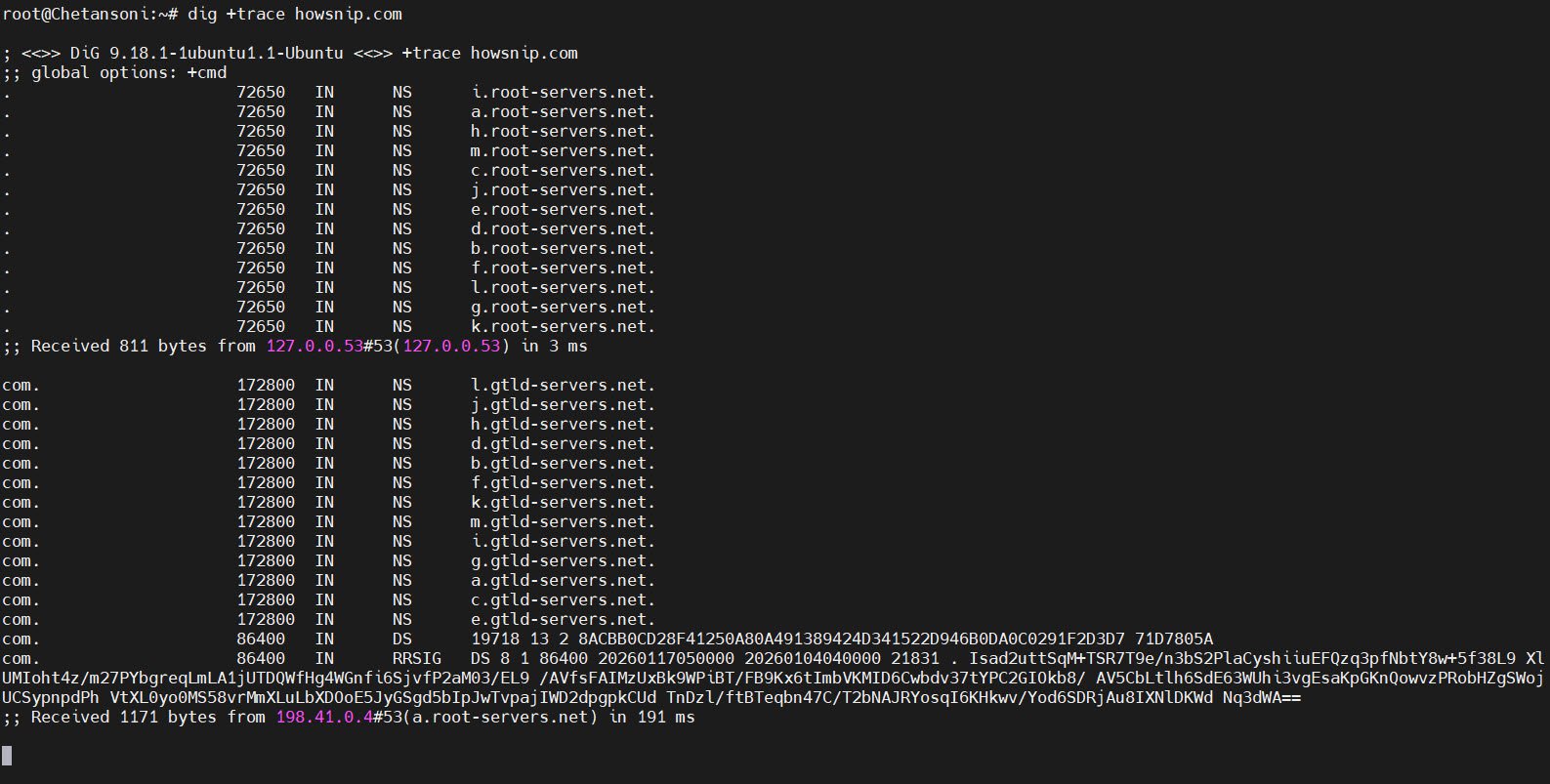
2.2 Short Output
If you want return only the resolved IP addresses, omitting extra details, then the command is:
dig +short example.com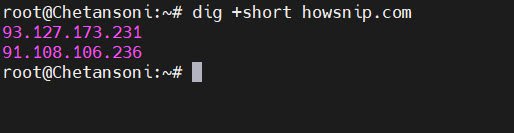
2.3 Display Only Answer Section
To show only the answer section for cleaner output, the command is:
dig +noall +answer example.com any
2.4 Reverse Lookup (PTR)
To perform a reverse DNS lookup, the command is:
dig -x +short IP
2.5 Name Server Search
To check the authoritative name servers and DNS consistency, the command is:
dig +nssearch example.com
2.6 Minimal A Record Output
In case, if you want to suppresses unnecessary output and displays only A record answers, then the command is:
dig +nocmd +noall +answer a example.com3. WHOIS Command Examples
The `whois` command retrieves domain and IP ownership information from public registries.
3.1 Domain WHOIS Lookup
To display domain registration details such as registrar, expiry date, and name servers, the command is:
whois example.com
3.2 IP Address WHOIS Lookup
To provide information about the organization or ISP that owns the IP address, the command is:
whois IP
Conclusion
When combined with real-world outputs, these commands become powerful learning and operational tools. Mastering them ensures faster issue resolution and deeper insight into how DNS infrastructure works.




