Did you know the Linux command line has been empowering users to interact with their systems for decades? Many Linux commands, like ls, cd, cp, and rm, trace their roots back to the original Unix systems of the 1970s, making them both powerful and time-tested tools.
Whether you’re a newcomer or an experienced user, working efficiently with Linux often means mastering the command line. This guide introduces a curated set of essential commands that help you manage files, directories, processes, networks, and your overall Linux system.
System administrators and developers heavily rely on these commands to automate tasks, manage users, monitor system health, and securely transfer files, making the command line an essential part of day-to-day work.
- uname -a
- uname -r
- uptime
- hostname
- hostname -i
- last reboot
- date
- cal
- w
- whoami
- finger user
- ls
- pwd
- cd
- mkdir
- rmdir
- rm
- cp
- mv
- cat
- touch
- clear
- ps
- man
- grep
- echo
- wget
- df
- top / htop
- kill
- find
- chmod
- ping
- history
1. uname -a
This command shows comprehensive system information including the kernel name, hostname, kernel version, hardware architecture, and operating system details. This command helps you quickly get an overview of your Linux environment.
Command: uname -a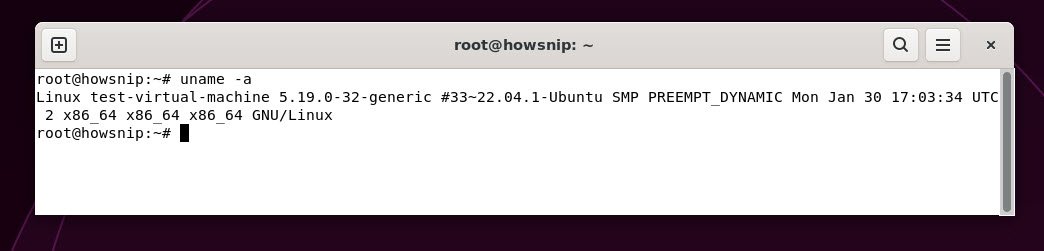
2. uname -r
If you want to check exactly which kernel your system is running, then you can use the following command:
Command: uname -r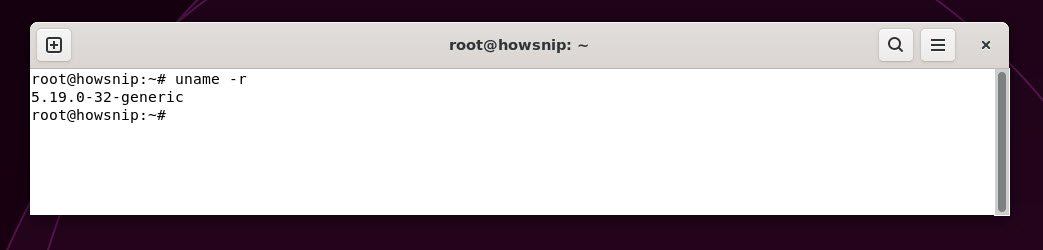
3. uptime
This command tells you how long the system has been running since the last reboot, the current time, how many users are logged in, and the system load averages for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes.
Command: uptime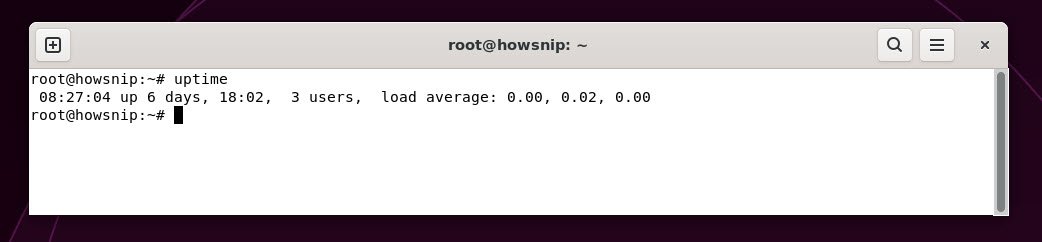
4. hostname
This command prints the network name of your computer, which identifies your machine on a network.
Command: hostname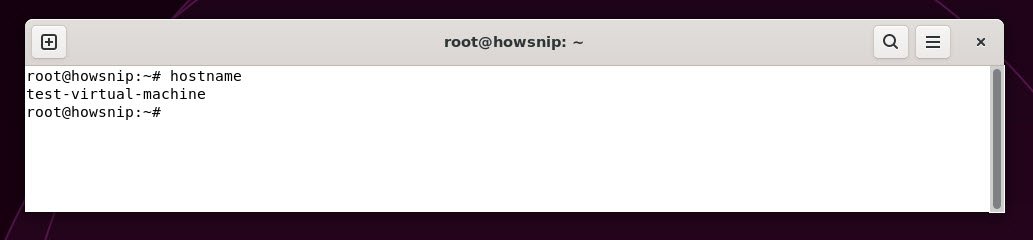
5. hostname -i
In case if you just want to display the IP address linked to your hostname, then the command is:
Command: hostname -i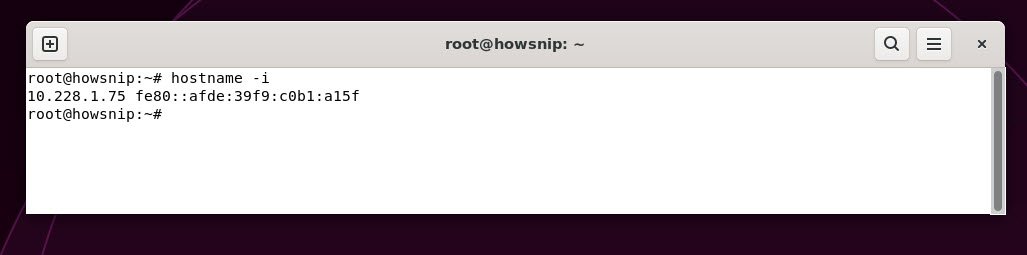
6. last reboot
This command lists system reboot history with dates and times. It shows when the system was restarted and can help in diagnosing unexpected restarts or server uptime.
Command: last reboot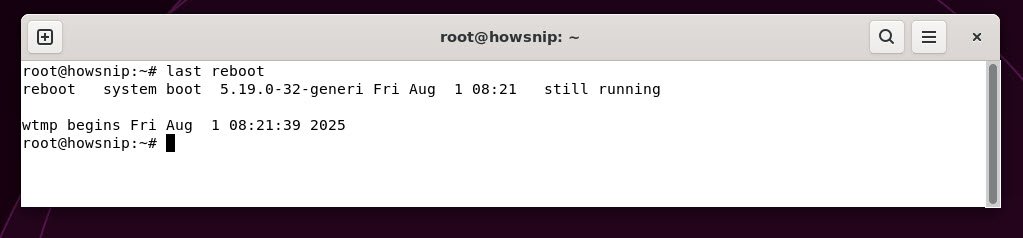
7. date
This command displays the current date and time according to the system clock.
Command: date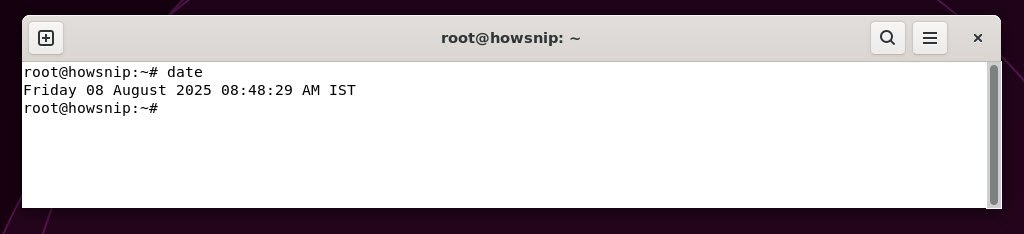
8. cal
This command shows a simple text calendar of the current month.
Command: cal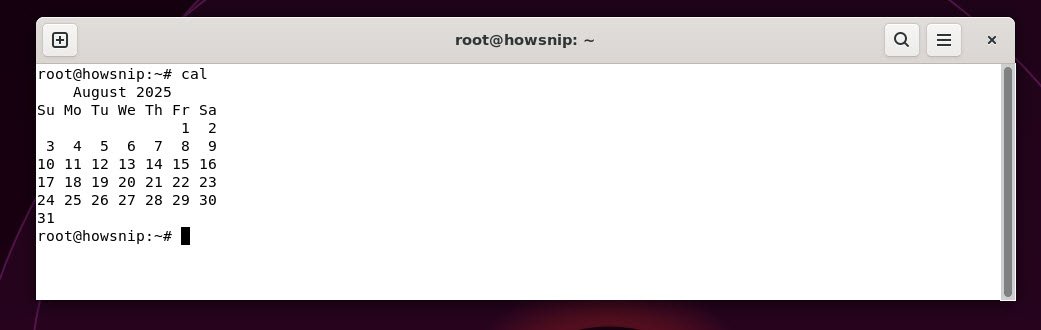
9. w
This command lists users currently logged in along with what command or process they are running. It also shows login time, idle time, and CPU usage, providing a snapshot of user activity.
Command: w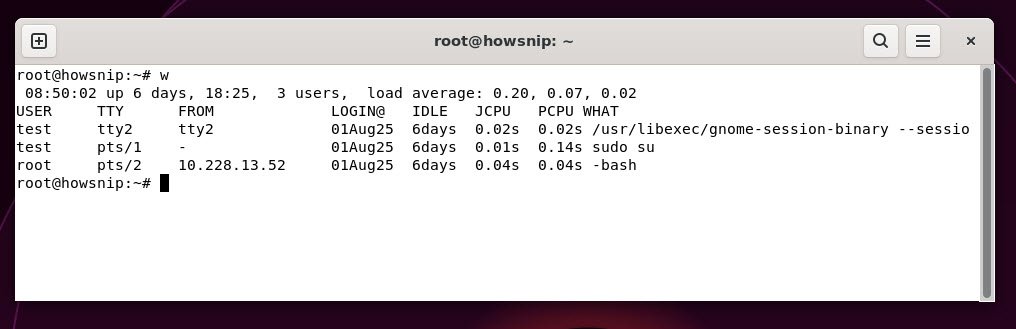
10. whoami
This command prints your current username to confirm which user account you’re operating under and is useful when working with multiple users or privileges.
Command: whoami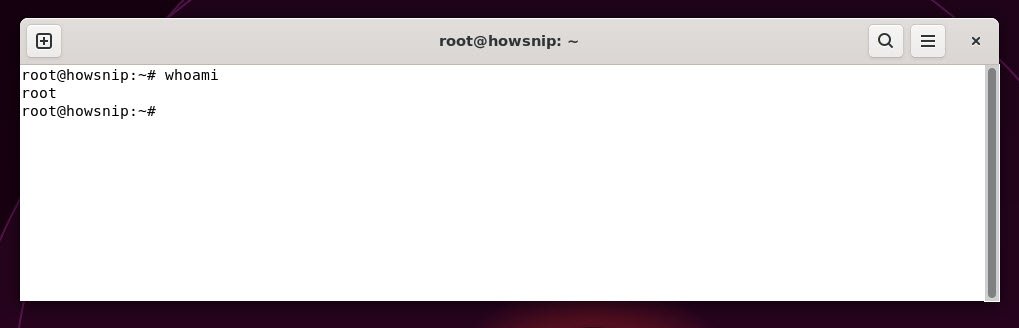
11. finger user
This command displays detailed information about a specified user, such as their full name, home directory, shell type, and whether they are logged in etc.
Command: finger root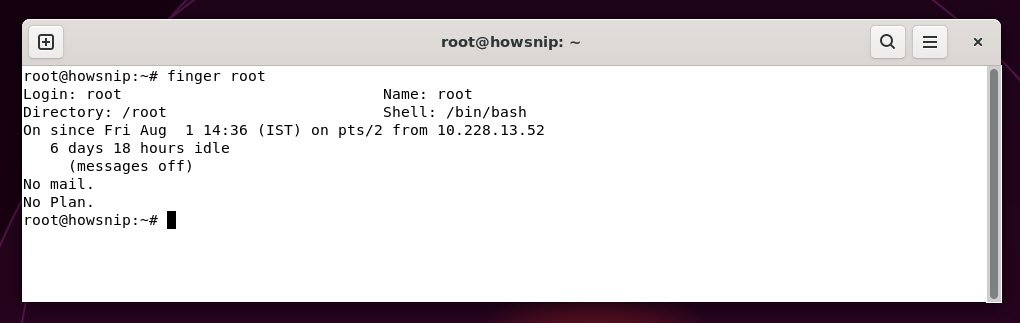
12. ls
This command lists files and directories in the current folder. It can be combined with options to show details like permissions, sizes, and modification dates.
Command: ls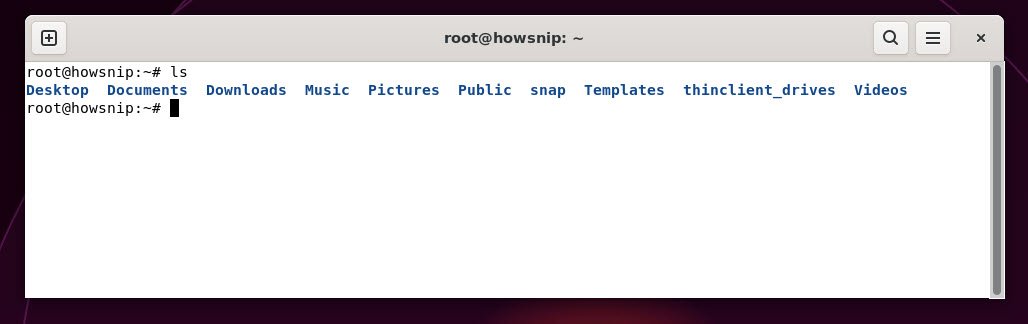
13. pwd
This pwd command shows the full path of your current location in the filesystem, useful to confirm where you are before running relative file commands.
Command: pwd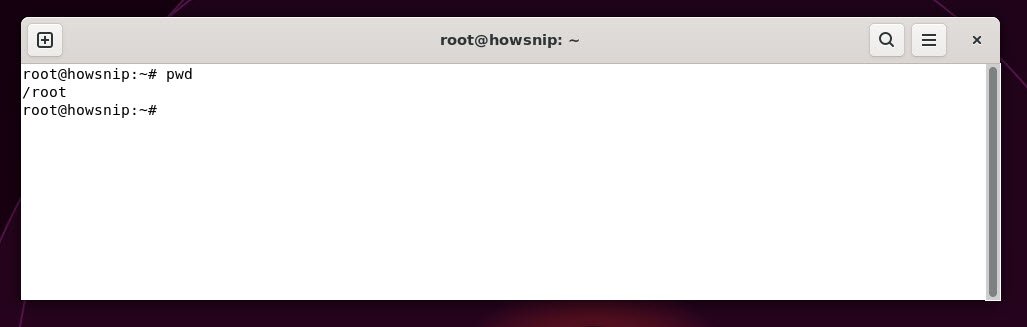
14. cd
This command changes the current directory to another. It helps you navigate the filesystem.
Command: cd /path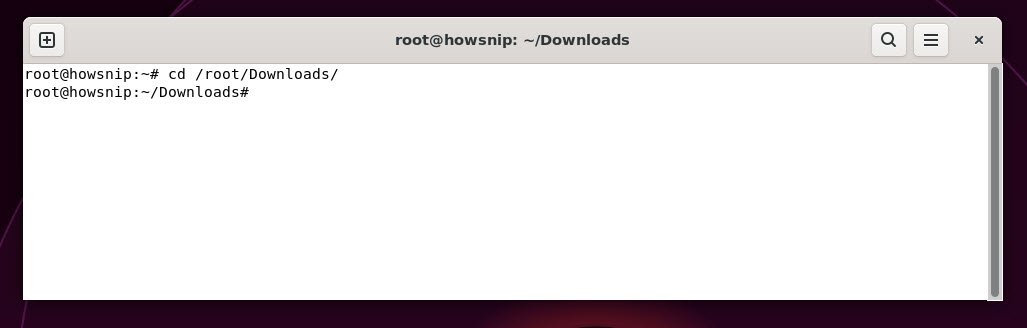
15. mkdir
This command creates a new directory (folder).
Command: mkdir <directory_name>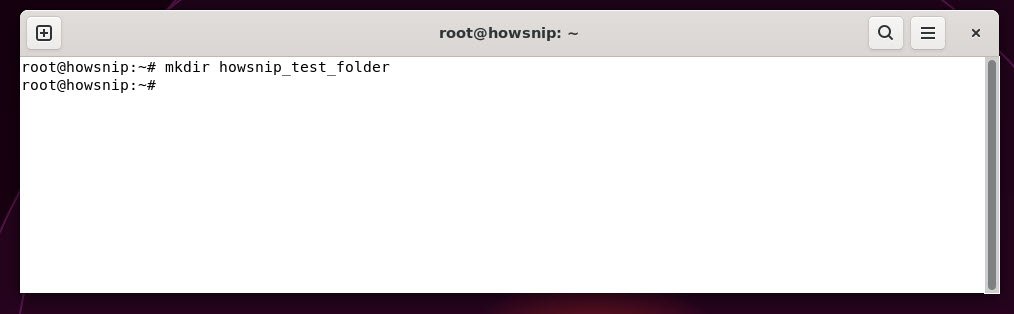
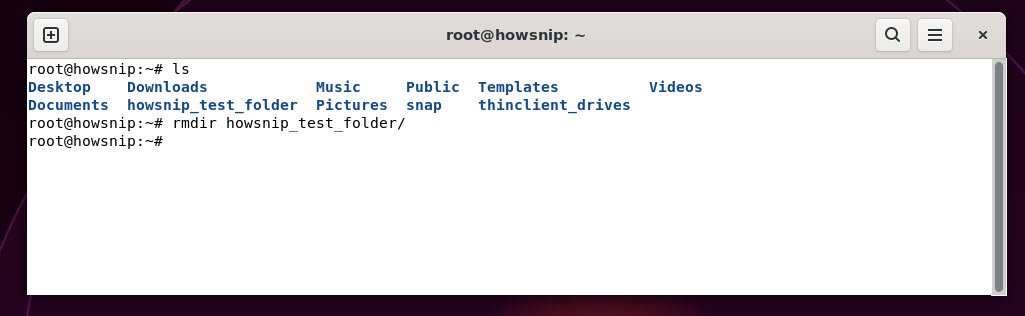
16. rmdir
To remove an empty directory, you can use the following command:
Command: rmdir <directory_name>If a directory contains files, you need other commands like rm with options to delete it.
17. rm
This command deletes files or directories (with options). Be cautious with this command because deleted files often cannot be recovered.
Command: rm -rf <file_name>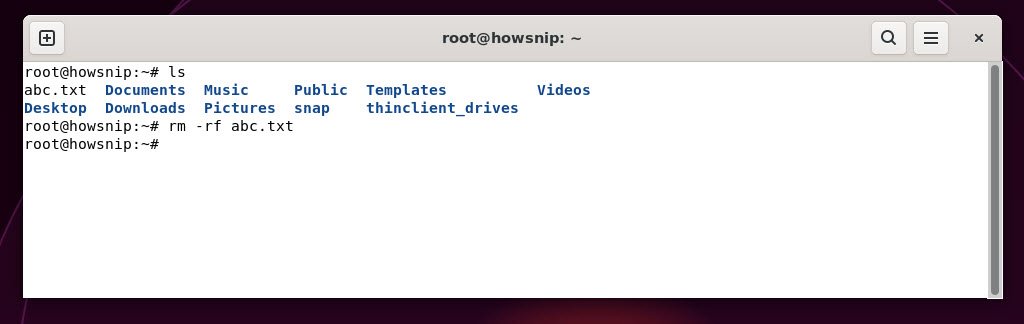
18. cp
This command copies files or directories from one location to another.
Command: cp <from_filename> <to_filename>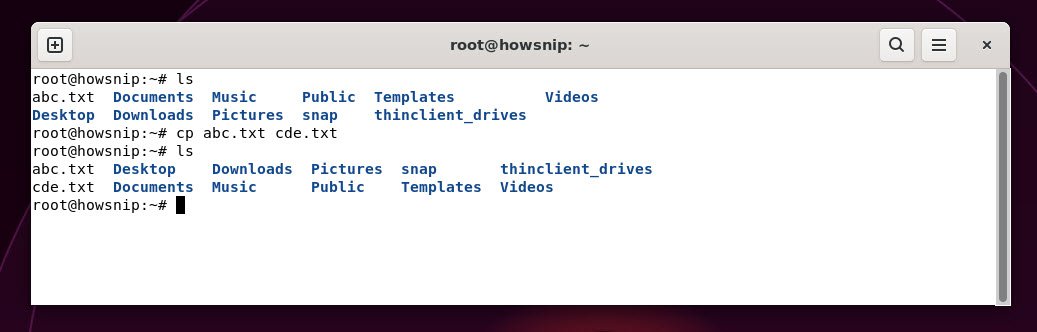
19. mv
This command moves or renames files and directories which is useful for organizing or renaming files without duplicating data.
Command: mv <from_filename> <to_filename>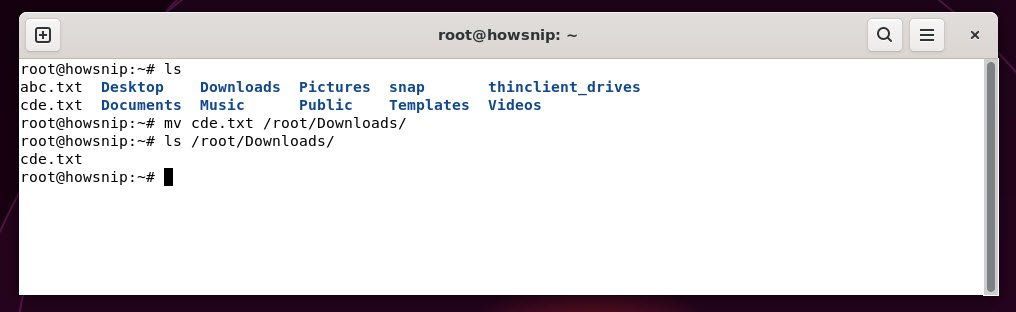
20. cat
This command displays the contents of a file in the terminal.
Command: cat <file_name>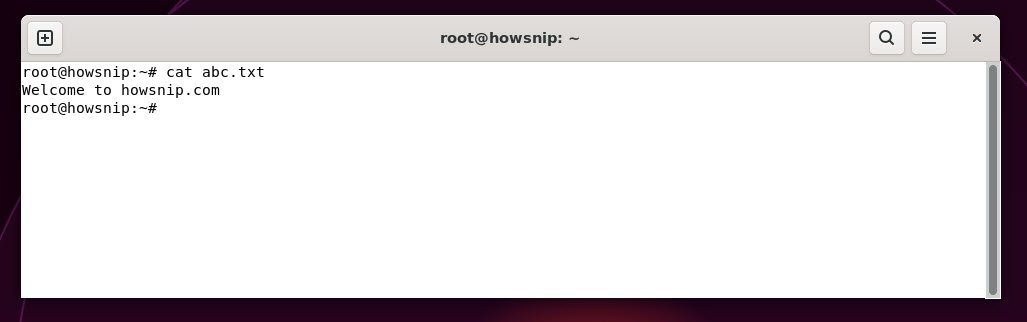
21. touch
This command creates an empty file or updates the timestamp on an existing file.
Command: touch <filename>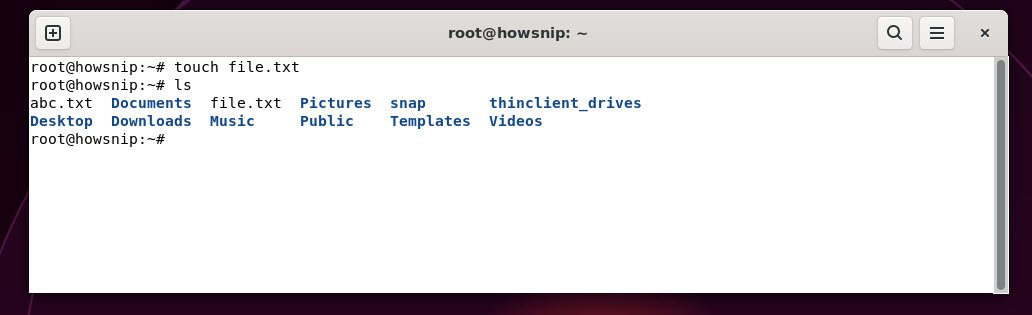
22. clear
This command clears the terminal screen to provide a clean workspace without previous command outputs cluttering the view.
Command: clear
23. ps
This command shows the current running processes for the user or system. This helps to monitor what programs are active at a given time.
Command: ps
Command: ps -aux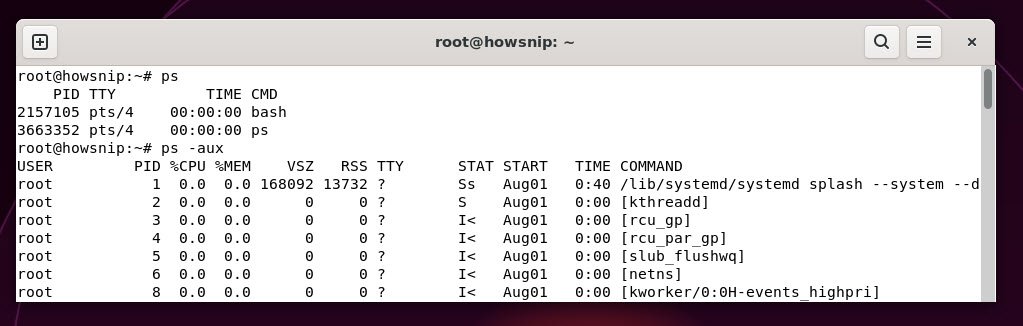
24. man
This command opens the “manual” pages for any command, giving you detailed descriptions, usage options, and examples for nearly all Linux commands.
Command: man <command>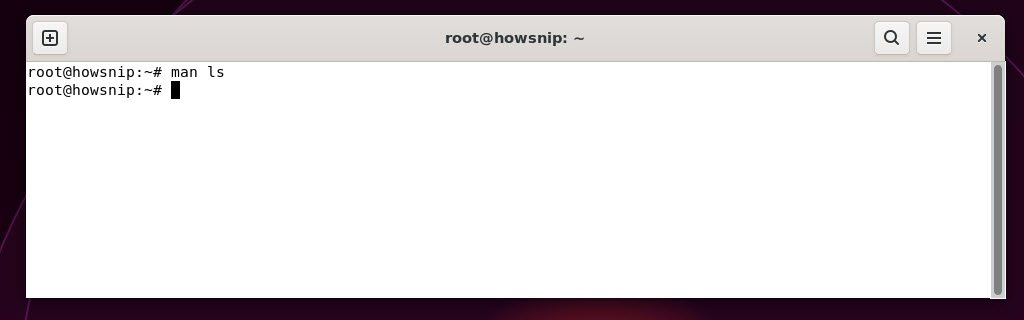
25. grep
This command searches text or command outputs for specific patterns or keywords.
Command: cat <file_name> | grep "text"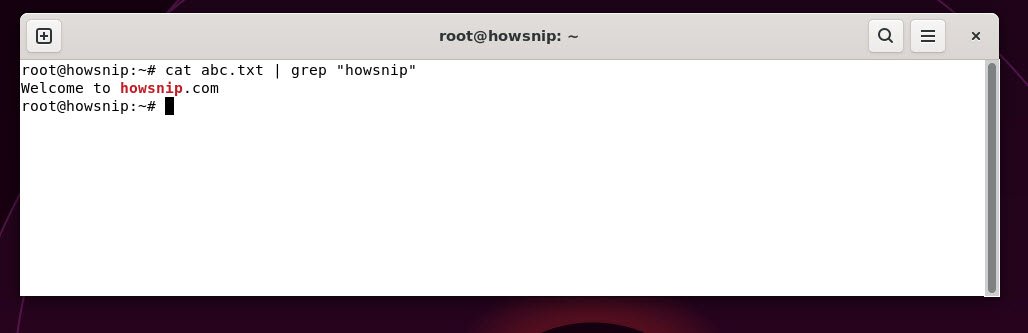
26. echo
This command prints text or variable values to the terminal which is used in scripts to display messages or output.
Command: echo "Text" >> <filename>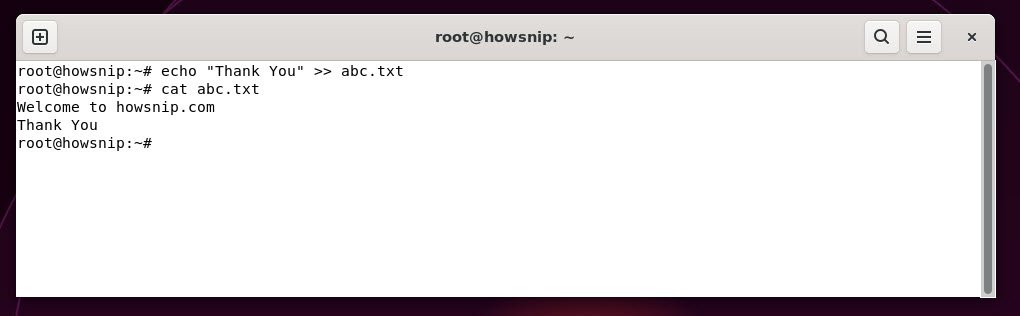
27. wget
This command downloads files or pages from the internet directly from the command line.
Command: wget <url>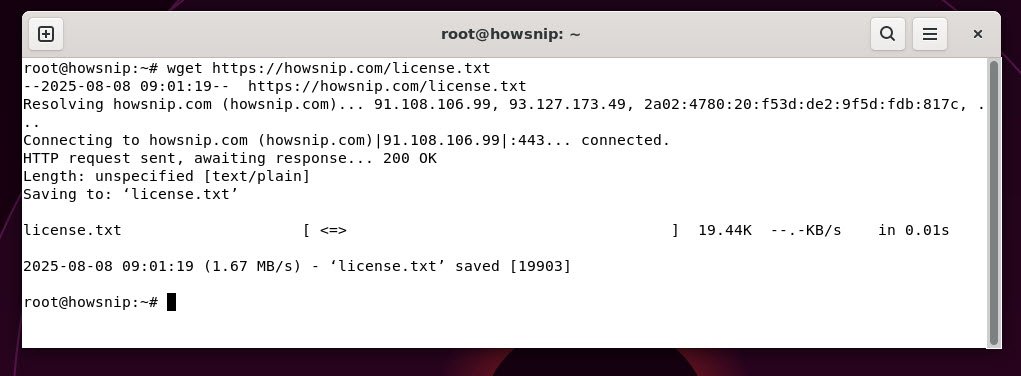
28. df
This command displays disk space usage for all mounted filesystems, showing total, used, and available space.
Command: df -h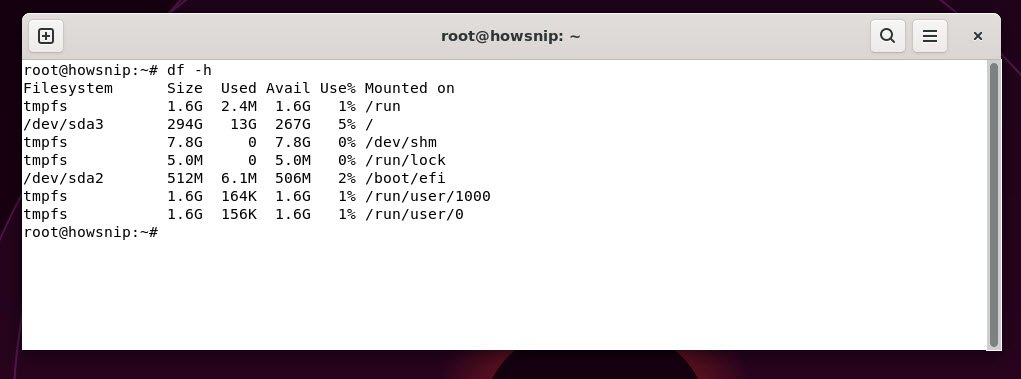
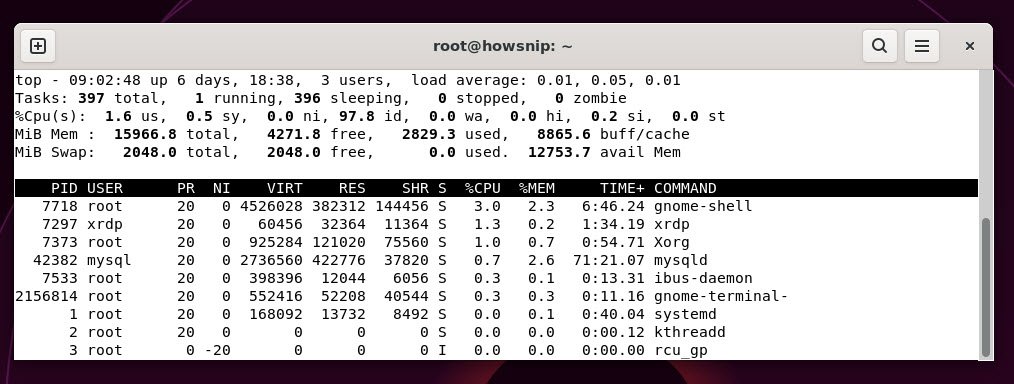
29. top / htop
This command displays a live, dynamic view of running tasks, CPU, memory usage, and other system resources.
Command: top`htop` is a more user-friendly alternative to `top` with navigation features.
30. kill
This command stops a running process by its process ID (PID) and is useful for shutting down unresponsive or unwanted tasks.
Command: kill -9 <pid>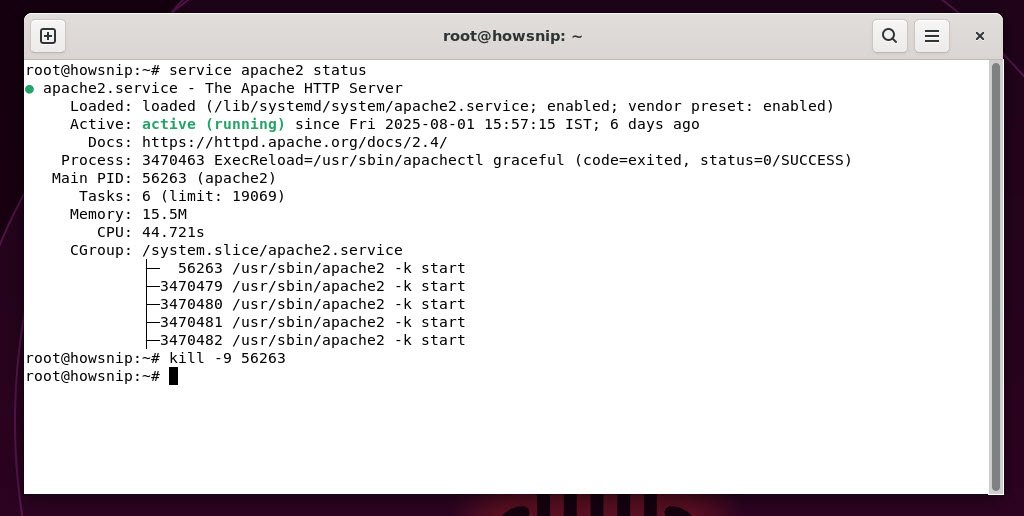
31. find
This command searches for files or directories matching specific criteria like name patterns, file size, or modification date.
Command: find . -name "filename"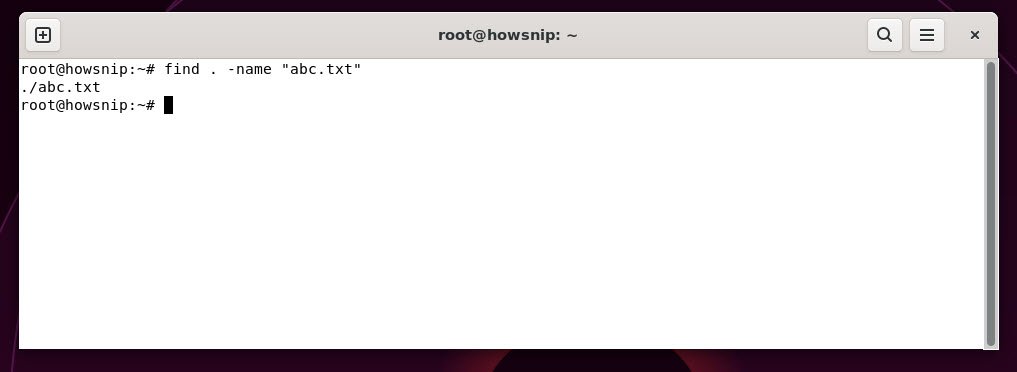
32. chmod
This command changes permissions of files or directories, controlling who can read, write, or execute them.
Command: chmod +x <filename>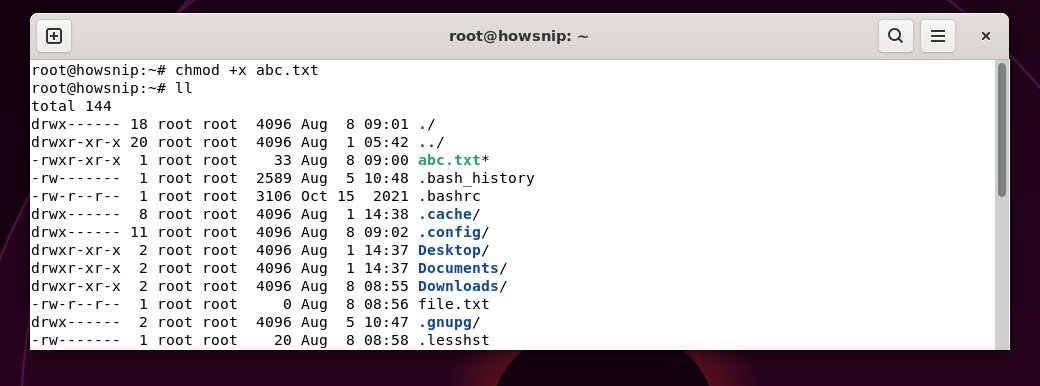
33. ping
This command tests network connectivity to another host by sending packets and measuring response time.
Command: ping <domain/ip>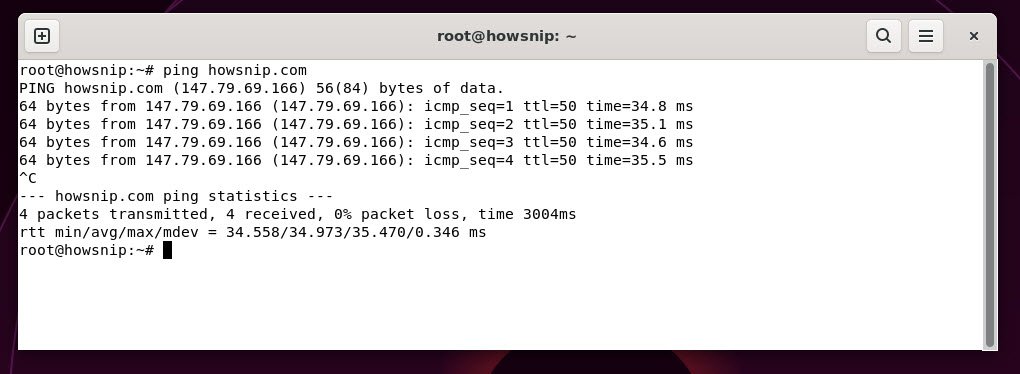
34. history
This command displays a list of commands you have recently executed.
Command: history